Key Points
- Stabilize ABCs; begin targeted evaluation without delaying life-saving therapy.
- Use system-specific risk tools to guide testing and disposition.
- Order high-yield tests first; escalate imaging when indicated.
- Start evidence-based initial therapy and reassess frequently.
Algorithm
- Primary survey and vitals; IV access and monitors.
- Focused history/physical; identify red flags and likely etiologies.
- Order system-appropriate labs and imaging (see Investigations).
- Initiate guideline-based empiric therapy (see Pharmacology).
- Reassess response; arrange consultation and definitive management.
Clinical Synopsis & Reasoning
HFrEF care integrates etiology identification, congestion assessment, and optimization of neurohormonal blockade. Evaluate volume status clinically and with natriuretic peptides, echo for EF and valvular disease, and ischemic evaluation when appropriate. Address triggers (AF with RVR, infection, nonadherence) and comorbidities impacting prognosis (CKD, diabetes).
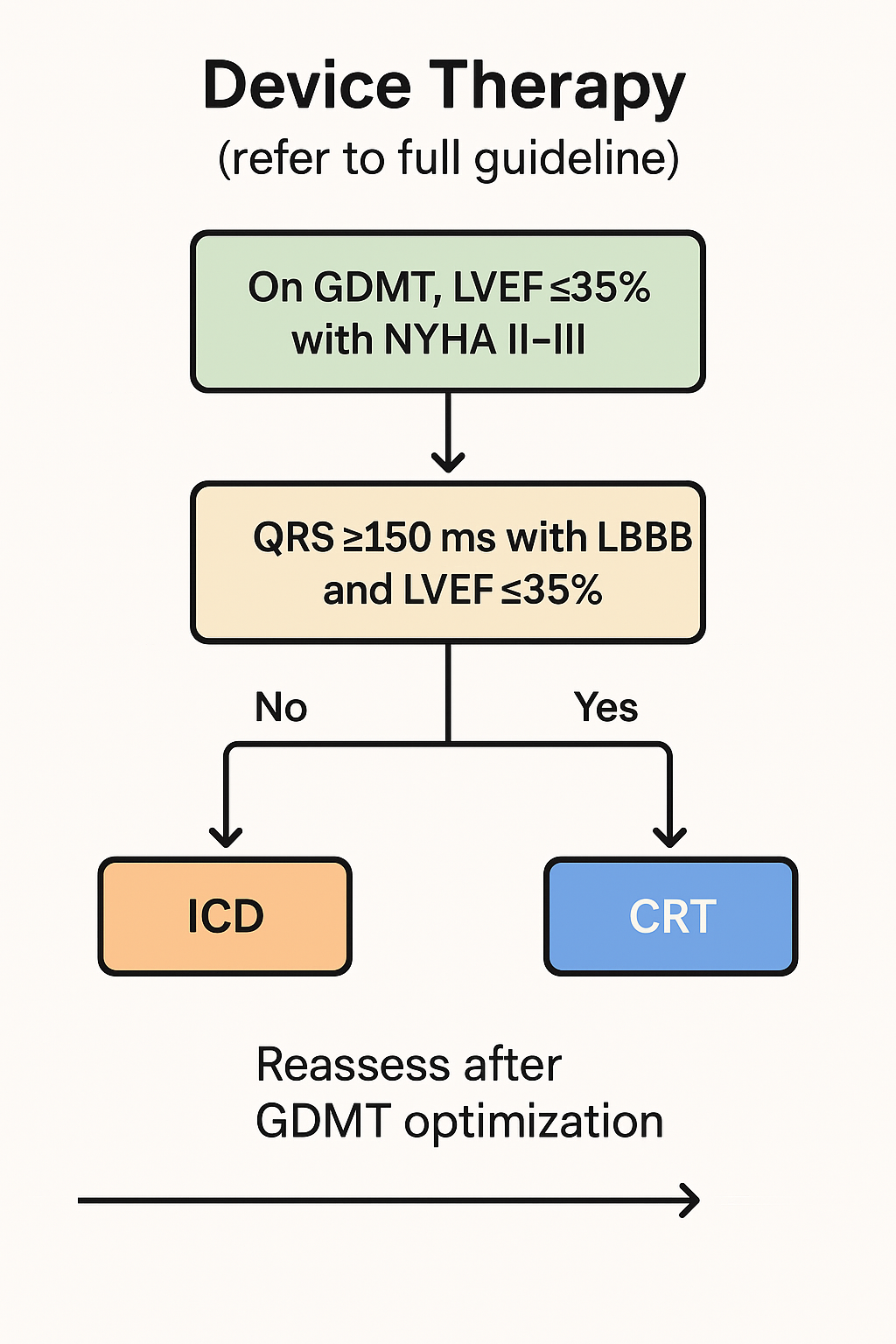
Treatment Strategy & Disposition
Initiate and uptitrate GDMT—ARNI/ACEi/ARB, evidence‑based β‑blocker, MRA, and SGLT2 inhibitor—while monitoring BP, renal function, and K⁺. Use loop diuretics to achieve and maintain euvolemia; consider hydralazine–nitrate in selected patients, device therapy per guidelines, and advanced therapies for refractory cases. Discharge planning includes sodium restriction, daily weights, vaccination, and cardiac rehab; admit for decompensation, escalating diuretic needs, or high‑risk features.
Epidemiology / Risk Factors
- Atherosclerotic risk (HTN, DM, HLD, smoking)
- Age/family history of premature CAD
Investigations
| Test | Role / Rationale | Typical Findings | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| EKG | Rhythm/ischemia | ST-T changes/arrhythmia | Serial |
| Troponin | Myocardial injury | Dynamic rise/fall | Trend |
| CXR | Pulmonary edema/size | Cardiomegaly/edema | |
| BMP/Mg2+ | Electrolytes/renal | Derangements | |
| CBC/Coags | Bleeding risk | Abnormal/INR |
Core GDMT Components
| Class | Examples | Key Monitoring |
|---|---|---|
| ARNI/ACEi/ARB | Sacubitril/valsartan; lisinopril | K, Cr, BP |
| β-blocker | Carvedilol, metoprolol succinate, bisoprolol | HR, BP |
| MRA | Spironolactone, eplerenone | K, Cr |
| SGLT2 inhibitor | Dapagliflozin, empagliflozin | Volume status, eGFR |
Pharmacology
| Medication | Mechanism | Onset | Role in Therapy | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist | Aldosterone blockade | Days | Mortality and hospitalization reduction | Hyperkalemia; gynecomastia (spironolactone); ED use |
| Beta-blocker (carvedilol/metoprolol succinate) | β1 blockade | Weeks | Mortality benefit | Bradycardia; titrate slowly; ED use |
| Sacubitril/valsartan | ARNI (RAAS/Neprilysin) | Days | GDMT for HFrEF | Hyperkalemia, hypotension; ED use |
| Loop diuretic | Na-K-2Cl inhibition (ascending limb) | Hours | Decongestion | Electrolyte loss, AKI; ED use |
| SGLT2 inhibitor | Renal SGLT2 blockade | Days | HF benefit regardless of diabetes | Euglycemic DKA (rare), GU infections; ED use |
Prognosis / Complications
- Prognosis by ischemic burden/LV function
- Arrhythmias and HF are complications
Patient Education / Counseling
- Explain red flags and when to seek emergent care.
- Reinforce medication adherence and follow-up plan.
Notes
Avoid non-DHP CCBs. Ensure vaccinations, sodium restriction, and cardiac rehab as appropriate.
Exhibits